02 纸张图像边框提取、摆正
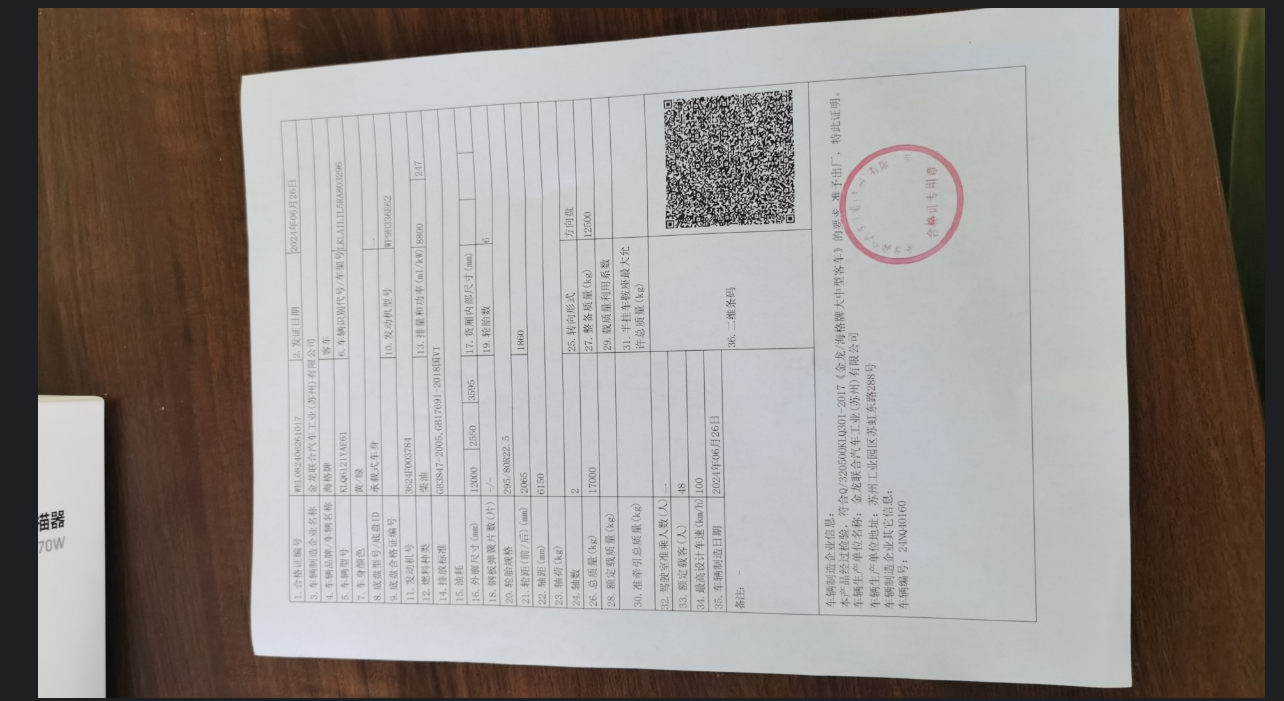
- 原始图片
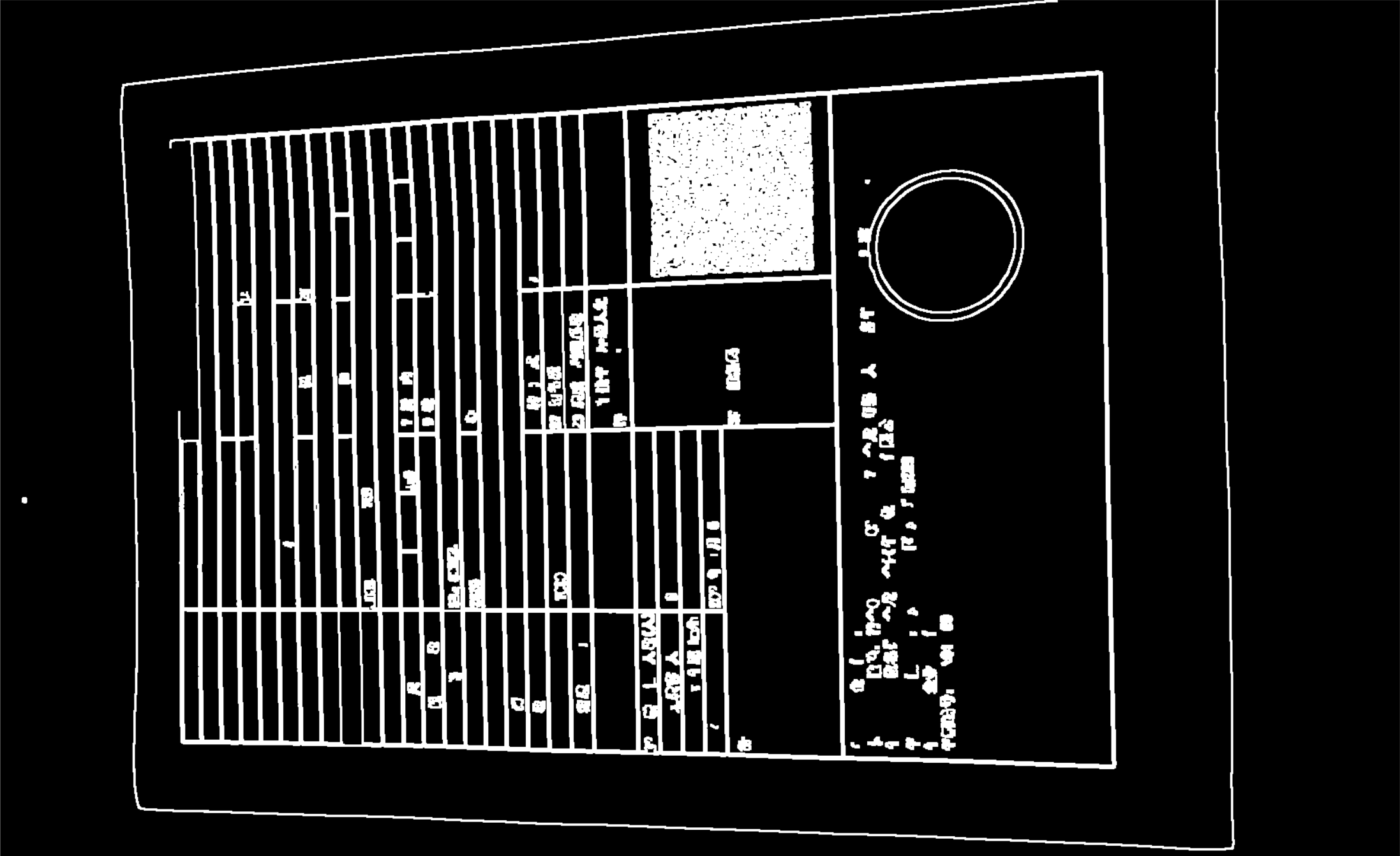
1.1 Canny函数边缘检测
这一步通过opencv的Canny函数将边缘提取出来(具体的功能介绍请自己查阅),值得一提的是在canny前为防止一些噪点必须通过高斯模糊去噪点,然后也膨胀边缘使图像更容易闭合
# 边缘检测
def getCanny(image):
# 高斯模糊
binary = cv2.GaussianBlur(image, (3, 3), 2, 2)
# 边缘检测
binary = cv2.Canny(binary, 60, 240, apertureSize=3)
# 膨胀操作,尽量使边缘闭合
kernel = np.ones((3, 3), np.uint8)
binary = cv2.dilate(binary, kernel, iterations=1)
return binary
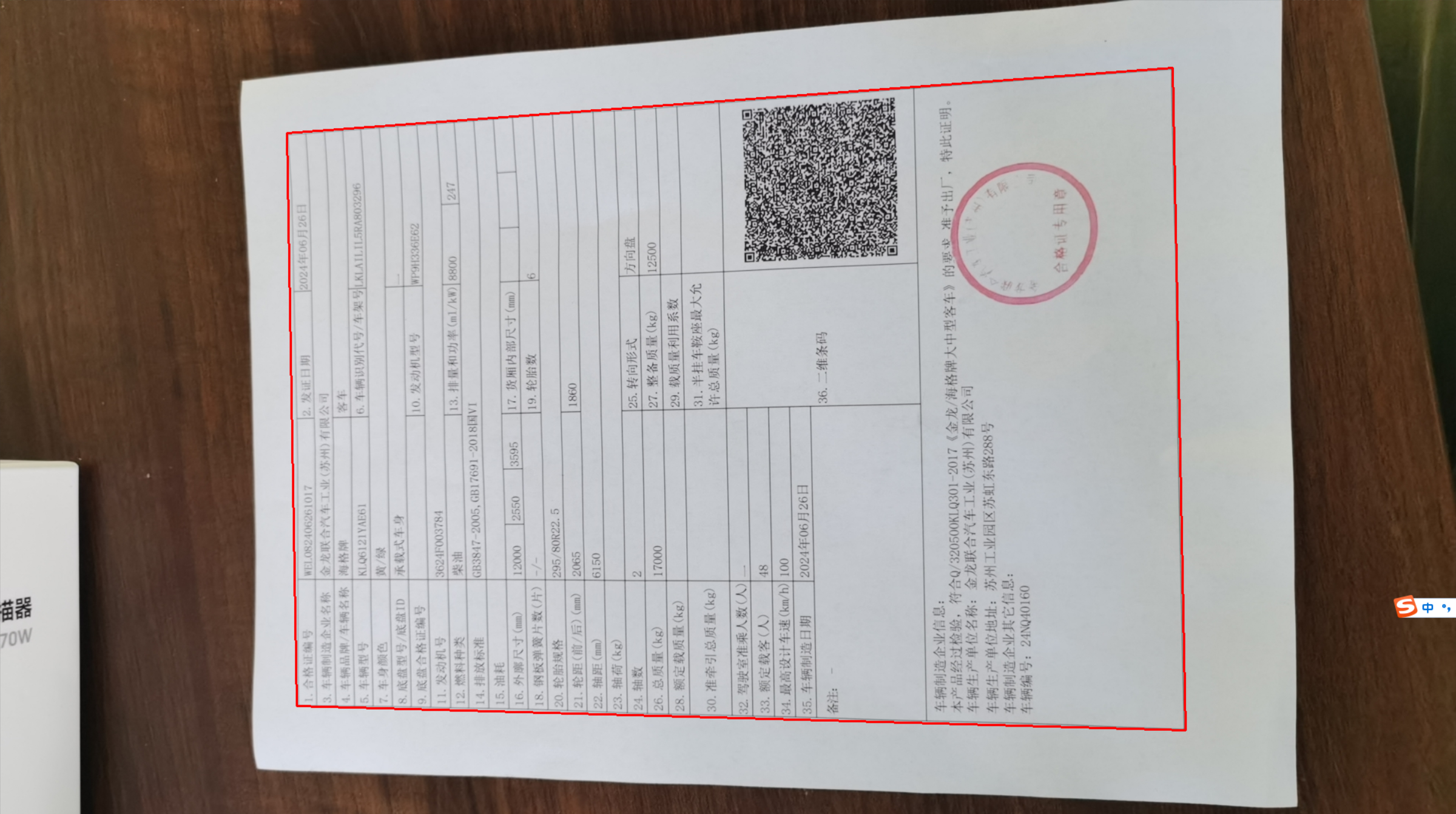
1.2 最大轮廓提取
通过findContours拟合出所有的轮廓,然后找出最大的轮廓即是纸质的边缘(因为拍摄的时候,我们的目标图形一般是最大的)
# 求出面积最大的轮廓
def findMaxContour(image):
# 对于 OpenCV 4.x 及以上版本
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(image, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
# 找到面积最大的轮廓
max_area = 0
max_contour = None
for contour in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(contour)
if area > max_area:
max_area = area
max_contour = contour
return max_contour, max_area
# 多边形拟合凸包的四个顶点
def getBoxPoint(contour):
# 多边形拟合凸包
hull = cv2.convexHull(contour)
epsilon = 0.02 * cv2.arcLength(contour, True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(hull, epsilon, True)
approx = approx.reshape((len(approx), 2))
return approx
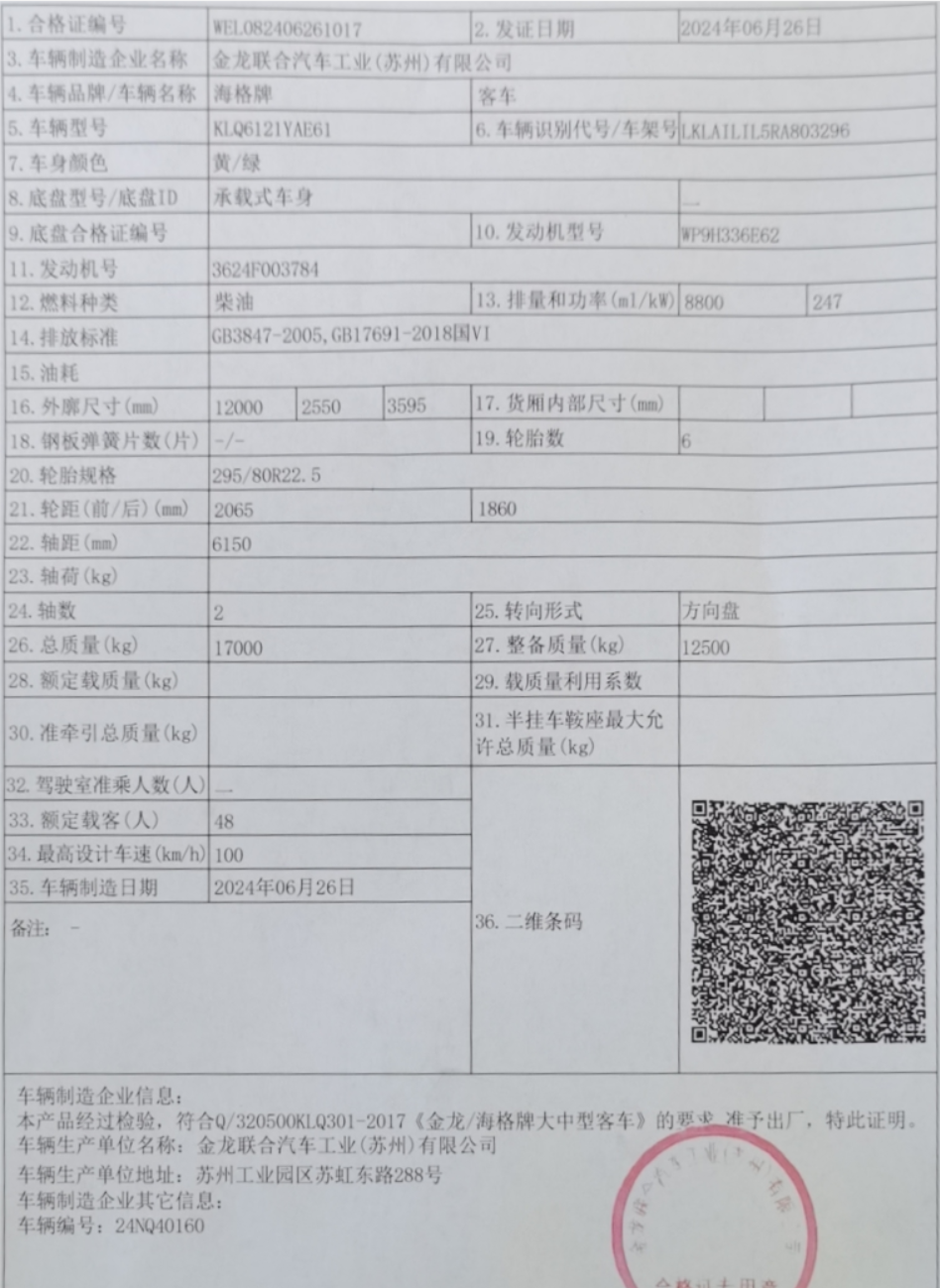
1.3 图像矫正
至此为止,我们都是在resize后的图片上找那四个顶点,我们还必须根据这4个点映射回原图的点。而且我们得到的图像是一个梯形形状,这时我们还要通过透视变化改成长方形的形状。
def Perspective_transform(box, original_img):
orignal_W = math.ceil(np.sqrt((box[3][1] - box[2][1]) ** 2 + (box[3][0] - box[2][0]) ** 2))
orignal_H = math.ceil(np.sqrt((box[3][1] - box[0][1]) ** 2 + (box[3][0] - box[0][0]) ** 2))
pts1 = np.float32([box[0], box[1], box[2], box[3]])
pts2 = np.float32(
[[int(orignal_W + 1), int(orignal_H + 1)], [0, int(orignal_H + 1)], [0, 0], [int(orignal_W + 1), 0]])
# 生成透视变换矩阵;进行透视变换
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(pts1, pts2)
result_img = cv2.warpPerspective(original_img, M, (int(orignal_W + 3), int(orignal_H + 1)))
return result_img
1.4 完整代码
# _*_ coding: utf-8 _*_
"""
Time: 2024/9/22 上午9:58
Author: EasonShu
Version: V 0.1
File: clipper.py.py
Describe:
"""
import math
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import cv2
import numpy as np
# 固定尺寸
def resizeImg(image, height=1920):
h, w = image.shape[:2]
pro = height / h
size = (int(w * pro), int(height))
img = cv2.resize(image, size)
return img
# 边缘检测
def getCanny(image):
# 高斯模糊
binary = cv2.GaussianBlur(image, (3, 3), 2, 2)
# 边缘检测
binary = cv2.Canny(binary, 60, 240, apertureSize=3)
# 膨胀操作,尽量使边缘闭合
kernel = np.ones((3, 3), np.uint8)
binary = cv2.dilate(binary, kernel, iterations=1)
return binary
# 求出面积最大的轮廓
def findMaxContour(image):
# 对于 OpenCV 4.x 及以上版本
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(image, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE)
# 找到面积最大的轮廓
max_area = 0
max_contour = None
for contour in contours:
area = cv2.contourArea(contour)
if area > max_area:
max_area = area
max_contour = contour
return max_contour, max_area
# 多边形拟合凸包的四个顶点
def getBoxPoint(contour):
# 多边形拟合凸包
hull = cv2.convexHull(contour)
epsilon = 0.02 * cv2.arcLength(contour, True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(hull, epsilon, True)
approx = approx.reshape((len(approx), 2))
return approx
def Perspective_transform(box, original_img):
orignal_W = math.ceil(np.sqrt((box[3][1] - box[2][1]) ** 2 + (box[3][0] - box[2][0]) ** 2))
orignal_H = math.ceil(np.sqrt((box[3][1] - box[0][1]) ** 2 + (box[3][0] - box[0][0]) ** 2))
pts1 = np.float32([box[0], box[1], box[2], box[3]])
pts2 = np.float32(
[[int(orignal_W + 1), int(orignal_H + 1)], [0, int(orignal_H + 1)], [0, 0], [int(orignal_W + 1), 0]])
# 生成透视变换矩阵;进行透视变换
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(pts1, pts2)
result_img = cv2.warpPerspective(original_img, M, (int(orignal_W + 3), int(orignal_H + 1)))
return result_img
if __name__ == '__main__':
img_path = './images/img_6.png'
image = cv2.imread(img_path)
# # 图像缩放 1920* 1080
# image = resizeImg(image)
binary_img = getCanny(image)
max_contour, max_area = findMaxContour(binary_img)
boxes = getBoxPoint(max_contour)
warped = Perspective_transform(boxes,image)
cv2.imshow('warpImage', warped)
cv2.waitKey(0)